by Dr. Corinna Frances Cabanilla
During ABS-CBN’s Harapan 2013
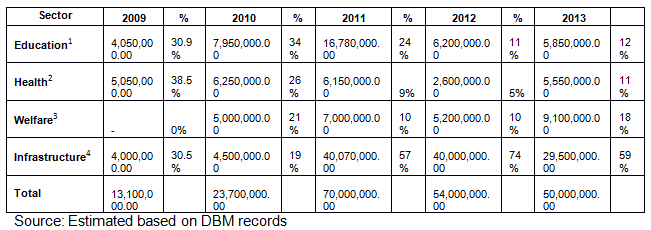
Estimating the distribution of Sonny Angara’s PDAF based on Department of Budget and Management PDAF releases reveals the following:
- For 2009, Sonny Angara’s PDAF amounts to PhP 13,100,000. Of this amount, 31% is allotted for education, 39% on health and 31% on infrastructure.
- For 2010, the records show that out of his PhP 23,700,000.00 PDAF, 34% was spent on education, 26% on health, 21% on welfare and 19% on infrastructure.
- For 2011, Angara’s PhP 70,000,000 PDAF was allotted to education (24%), health (9%), welfare (10%) and infrastructure (57%).
- For 2012, his PhP 54,000,000.00 PDAF was distributed as follows: 11% education, 5% on health, 10% on welfare and 74% on infrastructure
- For 2013, out of the PhP 50,000,000.00 PDAF, 12% was allotted for education, 11% on health, 18% on welfare and 59% on infrastructure
[1] Education includes financial assistance for implementation of scholarships and education programs and projects (ie. Alternative Learning System, sports-related/ sports development programs and projects, seminars, trainings)
[2] Health includes financial assistance for indigent patients (confined or out-patients) and
[3] Welfare includes financial assistance for indigent patients, displaced families, senior citizens, relief assistance and other social services
[4] Infrastructure includes construction, repair and/ or rehabilitation/ improvement of physical structures (ie. FTMR, flood control, multi-purpose buildings, roads, pavements, drainage, bridges, water systems, classrooms
Corrina Frances Cabanilla, PhD is a professor at the National College of Public Administration and Governance (NCPAG), UP Diliman. She also works at the Center for Policy and Executive Development (CPED).